
China’s Living Standards Will Continue to Rise
For 2019, Chinese GDP growth could eventually achieve around 6.2 percent in full-year growth, assuming policymakers succeed in the challenging balancing act to sustain higher-quality growth while suppressing faster debt accumulation.
Amid the Christmas meltdown, the Dow Jones plunged to less than 22,000 points, the lowest since September 2017. Thereafter, it soared over 1,000 points; the biggest single-day point gain ever. Nevertheless, it has declined 4,000 points in two months.
It is this historical market volatility associated with the Trump administration that now overshadows the world economy and China. In recent weeks, the U.S. economy has become increasingly exposed to policy mistakes and drastic market fluctuations.
In 2019, the Chinese economy will have to cope with great international uncertainty and even more extraordinary market volatility.
Short-term Fluctuations Versus Longer-term Trends
Recently, the New York Times reported that China was amid “a steep downturn.” Indeed, since the U.S. trade wars last spring, there has been much chatter in the West about the “China’s economic slowdown.”
Once again, uninformed observers have focused on quarterly growth, at the expense of annualized growth. In this regard, 2018 was an exceptional year in China and elsewhere. In the first half, global recovery was still gaining ground. In the second half, Trump’s trade wars caused substantial collateral damage that will be felt even more in 2019, in the absence of a constructive reconciliation.
Yet, China’s growth forecast for 2018 remains at around 6.7 percent, after a strong first half. Moderation will ensue in the second half and especially in 2019, depending on U.S. tariffs and slower demand worldwide.
For 2019, Chinese GDP growth could eventually achieve around 6.2 percent in full-year growth, assuming policymakers succeed in the challenging balancing act to sustain higher-quality growth while suppressing faster debt accumulation.
The government’s GDP growth target, which may be formally announced in March, is likely to reflect steady deceleration, due to international headwinds, particularly the ongoing trade wars; and domestic pressures, such as demographics, slowing cyclical growth, and other environmental, debt and real estate market issues.
However, such deceleration is normal after years of rapid industrialization and growth acceleration.
Decelerating Growth, But Rising Incomes
If the Chinese government ignored its commitment to poverty eradication, higher living standards and sustainability, it could achieve more rapid growth, but at the cost of people’s livelihood and environment.
On the other hand, policymakers cannot accept too much deceleration either. While the country’s economic growth is decelerating, Chinese living standards should continue to rise. The effort to double average incomes – as measured by GDP per capita, with purchasing power parity – between 2010 and 2020 requires growth to remain at around 6.1 percent in 2019-2020.
Chinese growth rate is currently positioned to decelerate from 9.6 percent to 5.6 percent between 2008 and 2023. Despite this deceleration, living standards will almost double. In 2008, Chinese GDP per capita was less than US$7,900. By 2023, it could increase to more than US$21,200.
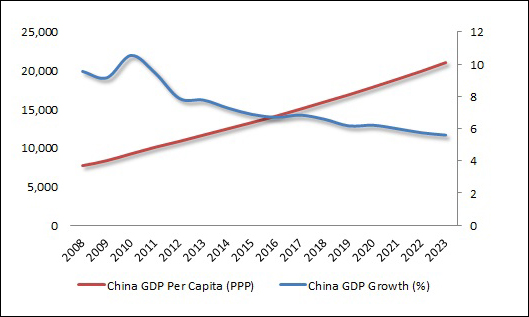
Furthermore, since current growth is around 6.5 percent, policy authorities are likely to prefer gradual deceleration, which fosters stability, over more abrupt slowing growth, which is perceived as disruptive.
Finally, China’s potential growth continues to indicate that a growth rate that exceeds 6.0 percent is achievable and viable, though not an easy task in the current international environment.
The government is likely to prefer supportive fiscal policy as the primary tool to ensure stable growth. In this quest, fixed investment, particularly infrastructure, is expected to play a key role when consumption and export growth are likely to slow – the former due to increasing consumer caution, the latter due to the trade wars.
China’s monetary stance is likely to remain accommodative, which implies a mild, but manageable rise with inflation (closer to 2.5 percent rather than 2.2 percent in 2018). Consequently, the Chinese yuan is likely to soften against the U.S. dollar.

While Washington is pushing for abrupt changes in Chinese economic policies, Beijing will stay the course. In practice, policy focus will continue to shift from cyclical stimulus and debt-fueled growth toward structural reforms, higher-quality growth and the rebalancing of Chinese economy from investment and exports toward consumption and innovation by 2030.
Most Challenging International Headwinds
Over the next year, it is possible that U.S. trade wars may broaden dramatically from exports to investment and intellectual property. Nevertheless, the global recovery that began in the West in the aftermath of the global crisis of 2008 (thanks in great part to China’s dramatic growth through those years), is now set to slow down in 2019-20. In that scenario, the West would be heading toward a complicated, challenging and politically divisive stagnation.
Much of these downturn risks remain under-valued in the West. When the growth rate of the U.S. economy is slower than anticipated, that’s usually attributed to a “bad quarter.” It is not necessarily seen as a sign that the U.S. economy is in greater danger. Yet, in the case of China, such projections seem to be a norm, even though economic realities suggest otherwise.
So, while the international media systematically highlights downturn risks for China and other large emerging economies, it consistently downplays the magnitude of risks in the U.S. and other major advanced economies. Such discrepancies can have distressing implications.
These double standards foster the kind of gap between perceptions and realities that made the 2008 crisis so abrupt. However, a decade of quantitative easing and ultra-low rates has left the advanced economies far more vulnerable than China.
Dr Steinbock is an internationally recognized expert of the multipolar world economy, founder of Difference Group Ltd and has served at the India, China, and America Institute (US), Shanghai Institutes for International Studies (China) and the EU Center (Singapore).
Opinion articles reflect the views of their authors, not necessarily those of China Focus
Source: China.org.cn
 Facebook
Facebook
 Twitter
Twitter
 Linkedin
Linkedin
 Google +
Google +










